Bamboo Construction, Malaysia
Generalities
There are more than 1000 species. It takes only 5 years to get construction material in a tropical climate when you need decades for timber. It absorbs better CO2 and releases 35% more oxygen than equivalent stands of trees. Bamboo holds up to 12 tons of carbon dioxide from the air per hectare.It is the fastest-growing plant on earth. Some species in Japan expand 1 m a day. Bamboo is a giant grass, once cut out it sprouts back and can be harvested again.It is still suffering from misconceptions seen as the poor man’s timber. Nevertheless, it offers superior earthquake protection compared to wood or cement. Structural strength of bamboo is a great advantage; it has better performances as concrete. Steel stands are the reference but bamboo density remains 10 times lower. This is the reason it is often called the vegetal carbon.
Local circular economy and landscape regeneration
Inserting and cropping bamboo is a way to create nearby circular economy. It is very easy and affordable for low-income communities to grow and use this giant grass. Abary Earth in Nepal has been developing this concept, teaching locals how to plant, harvest and build with this natural material. It regenerates landscapes, provides jobs and earnings for the inhabitants. It recreates biodiversity that infiltrates rain waters, it fights against erosion, flooding and mud sliding, and as a result protects populations
Species
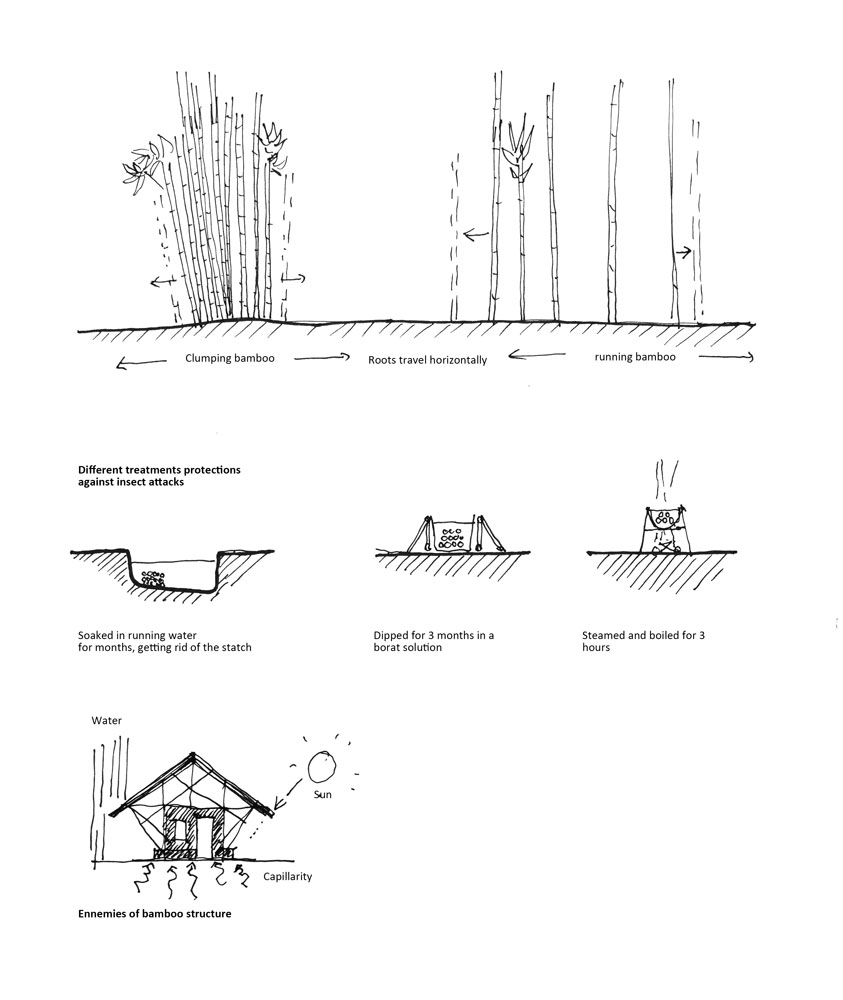
It exists 2 types of spread: the running and the clumping bamboo. This last one is easier to control, but in both case roots are travelling horizontally and this plant remains an invasive species.
Preservations
Bamboo without treatment will decay from insects and fungal attacks. The main goal is to get rid of the starch which attracts powder beetles, for example. The traditional method is to let the poles soak on the riverbed for months. Another option uses diffusion by dipping the material in a solution of borax and boric acid. For this the posts have to be pierced all the way for the mixture to be active all along. In case of little amount of time available, bamboos are boiled for 3 hours in the liquid.
Likewise wood, bamboo structures are extremely sensitive to water and sun. The design needs to protect the edifice from rain and direct UV that lead poles to crack. To avoid capillarity buildings must be elevated at least 15/20 cm on a dry fundament like brick beds or precast concrete.
Utilization
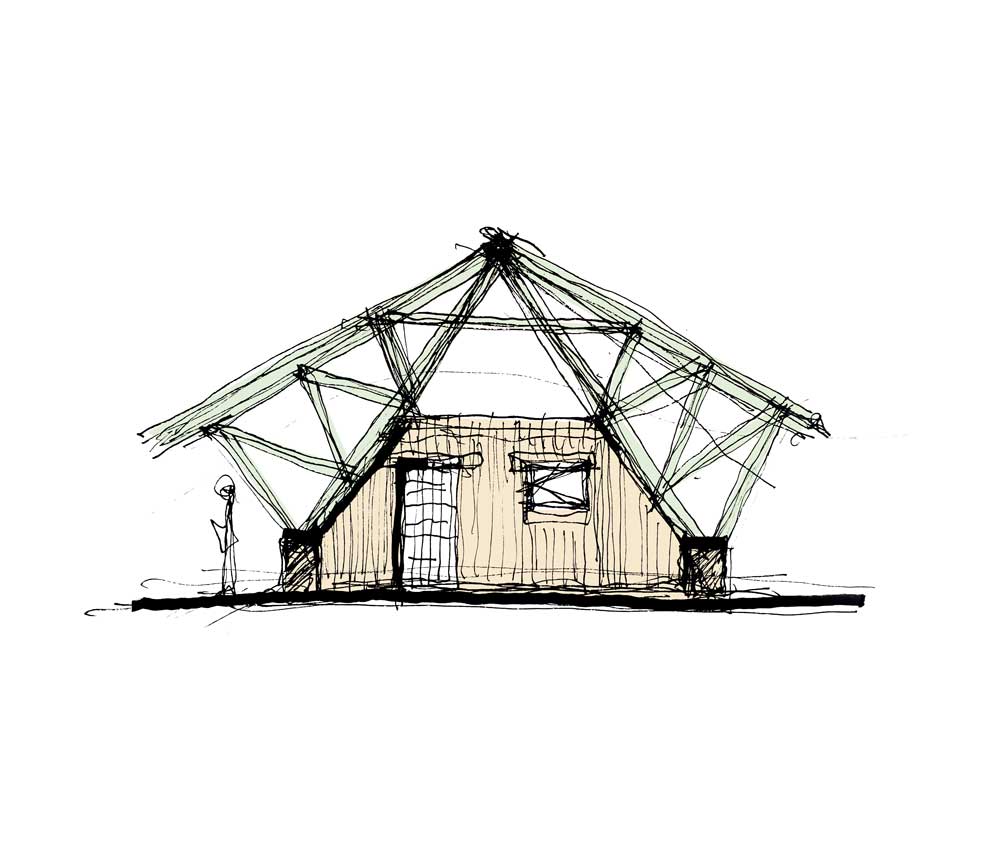
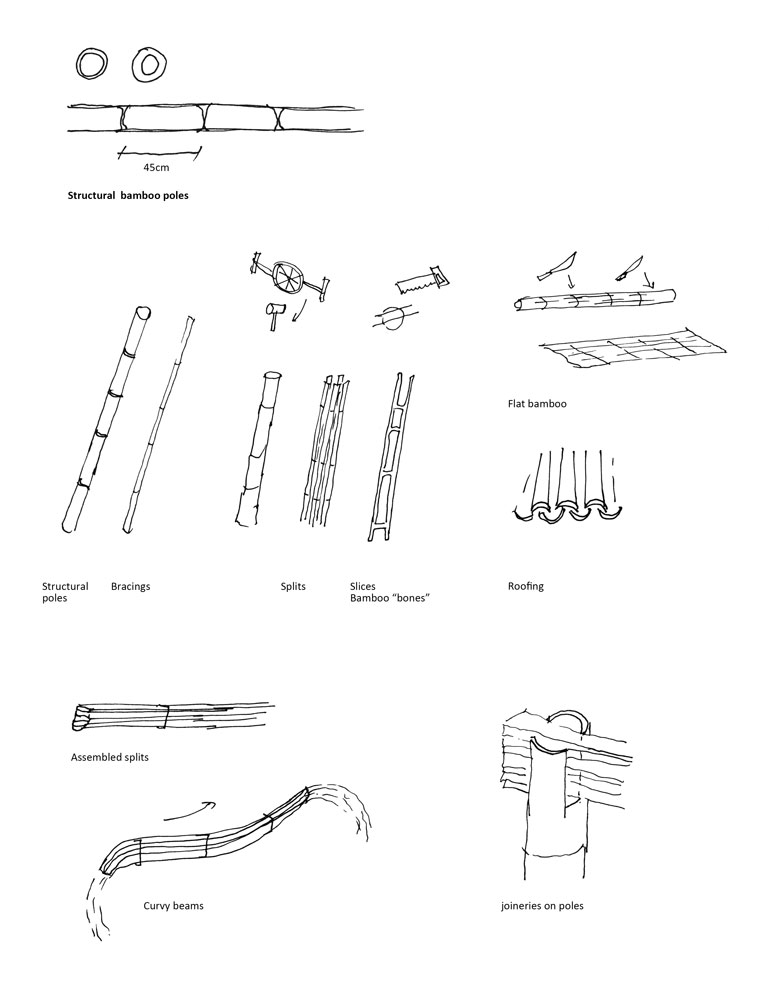
Bamboo can be employed for structural elements as columns, beams, trusses; the poles must have a minimum thickness and a distance between the knots must be more than 45 cm. It can as well be used for non-structural building components: walls, cladding, doors, windows, furniture. Traditionally, this giant grass is also exploited for temporary architectures, and for scaffolding.
The poles can be processed into splits; slices also called ‘bones’, and flat bamboo deployed for curvy surfacing for the roofing. Splits can be assembled into beams that can be arched thanks to the flexibility of this material. Similarly to wood, it is possible to laminate bamboo, into boards but also to create strong structural beams.
Bamboo skin can be utilised to be woven, to create handcrafts but also panels. That last one can be associate with clay coating with the example of the wattle and daub technique employed to set up a partition wall. Leaves and shoots can be used for medicine, beverages or food; the twigs for making clothes, the base parts for charcoal.
Construction Techniques
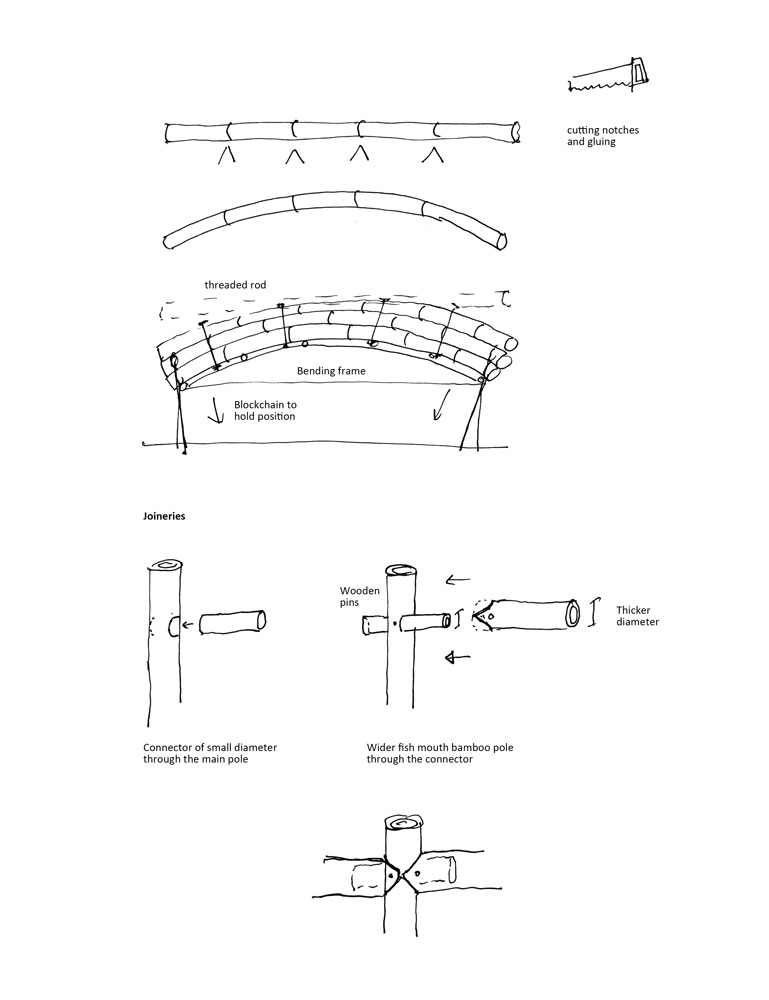
Bamboo poles can be cut off on their notches to force them into a rounded shape. For bigger structure and loading, several posts can be bend together, locked into position thanks to blockchains and threaded rods. The quickest modern way to attach elements is employing those metal pieces with nuts. Protection against rusting is a must.
More traditionally, the fish mouth joinery is really often used in construction as well as in furniture making. To reinforce it, a connector going through the main column can be placed in, both of the lateral bamboo poles are embedded in. Pins are then nailed in to block the position of the joint.
Tools that are used are simple: a sharp curved knife, a machete for the splitting, a handsaw, a gouge…